Organization
Related publications: [ROMA, ICML 2020; RODE, ICLR 2021]
We developed role-based learning, where agents learn their roles to decompose a complex task.
In the figure below, we show changes in roles of different agents in an episode. The role will decide the agent's behavior.
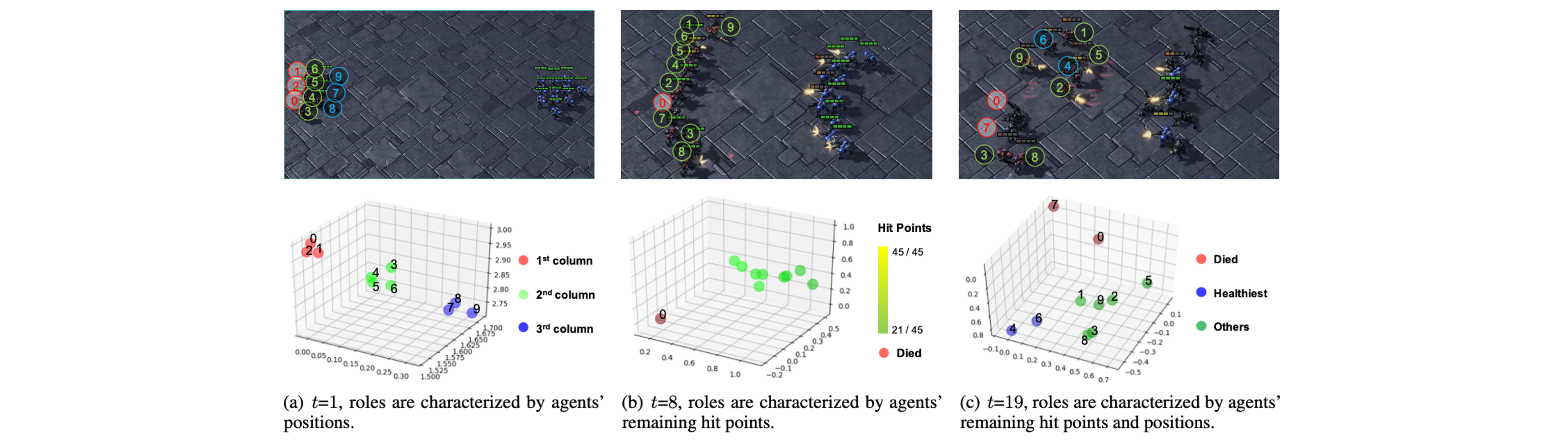
Communication
Related publications: [NDQ, ICLR 2020; Pragmatic Reasoning Communication, NeurIPS 2020]
We studied sparse, concise, but informative communication.
In the following figure, two agents start at a_4 and b_3, respectively, and they want to reach g simultaneously but can only observe its own state. To finish the task, they need to communicate their location to each other.
The second row shows our communication strategy. 0 means no communication. Agents learn to only send a bit when they are one step away from the goal state.
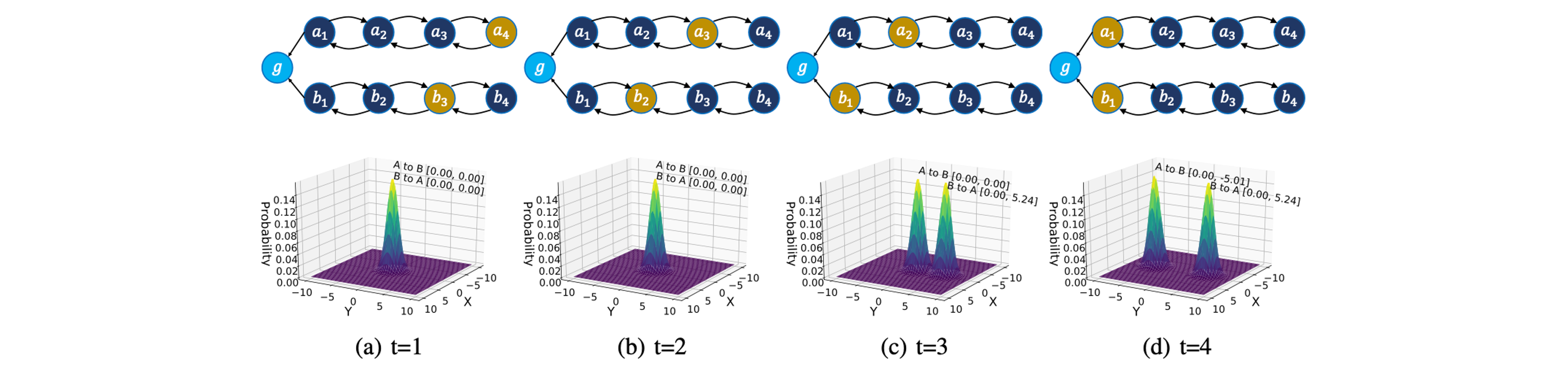
Diversity
Related publications: [CDS, NeurIPS 2021]
We find that diversity matters in multi-agent collaboration.
The following figure shows that our method learns versatile strategies by encouraging diversity in the difficult Google football tasks.
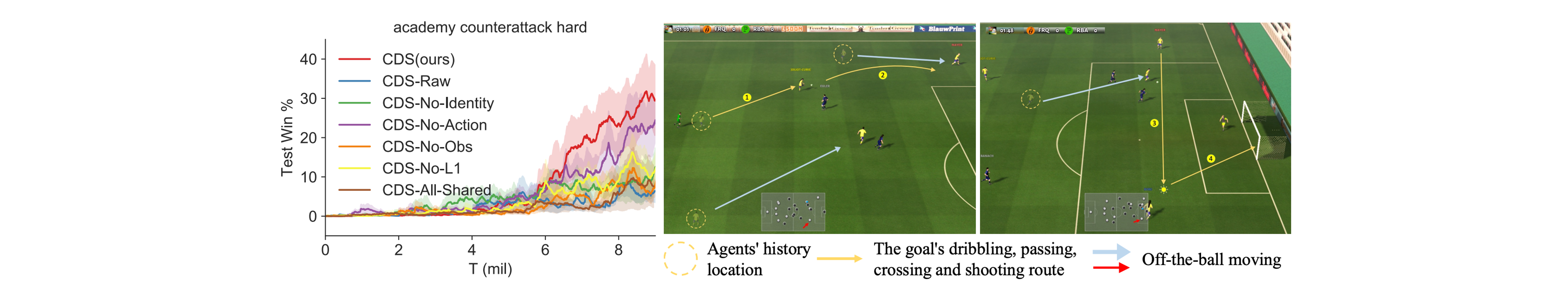
Coordination
Related publications: [NLCG, NeurIPS 2022; SOP-CG, ICML 2022; CASEC, ICLR 2022]
Coordination graphs: sparse, non-linear, and self-organized.
The following figure shows how the coordination structure could be adaptive: (a) Self-organized grouping at initialization; (b) Connecting to agent with rich observation for better information sharing; (c) Concentrated collaboration structure around an enclosed adversary.
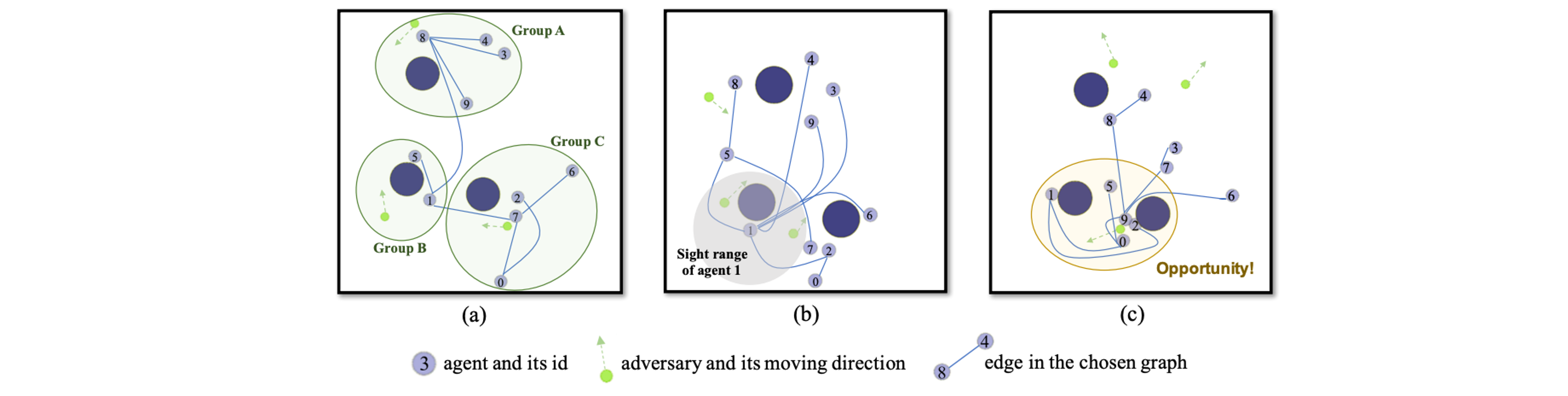
Exploration
Related publications: [EDTI, ICLR 2020]
We find that encourage agents' influence on each other can encourage exploration in large observation-action spaces.
Cooperation
Related publications: [DOP, ICLR 2020]
We developed a multi-agent policy gradient method with significant reduced variance.
Learning in Games
Related publications: [GA-SPP, AAMAS 2019]
This paper makes three major novelties. First, to our best knowledge, GA-SPP is the first gradient-ascent algorithm with a finite learning rate that provides convergence guarantee in general-sum games. Second, GA-SPP provides convergence guarantee in larger games than existing gradient-ascent algorithms, which include m × n positive semi-definite games, a class of 2 × n general-sum games, and 2 × 2 general-sum games. Finally, GA-SPP guarantees to converge to a Nash Equilibrium when converging in any m×n general-sum game.
Robustness
Related publications: [TRAM, NeurIPS Workshop 2022]
We study how to improve the robustness of multi-agent learning algorithms by attacking them during training time.
Transfer
Related publications: [MATTAR, NeurIPS Workshop 2022]
How to transfer the policy learned by one multi-agent team to another?.